本文由 简悦 SimpRead 转码, 原文地址 blog.csdn.net
前言
在数据同步见过 sqoop,datax,hdata,filesync,这四个工具。分析内部的实现逻辑各有巧思,也收获良多。 Sqoop1 和 sqoop2 底层数据同步的基本原理是一样的,所以我选择了 sqoop1 的源码作为分析的切入点。datax 和 hdata 在架构上大同小异,hdata 在数据传输借鉴了 Disruptor 一些内部实现,从 Disruptor 官网文档介绍让人对的原理及其感兴趣。好东西留待以后慢慢研究,所以选择 datax 更为一般的实现。filesync 是公司内部开发的一个文件同步工具,用于远程文件和 hdfs 的文件同步
Sqoop
导入
sqoop 从数据库同步到 hdfs 有俩种方式,1,JDBC 的连接。2,使用数据库提供的工具
我们以 mysql 为例子
同步过程分为三个步骤:1,对数据分片;2,读取数据;3,写入数据
JDBC
对数据分片采用通用方式,用 count 聚合函数获取需要同步的数据量 nums,获取设置的 map 数 m,nums/m 就是每个 map 需要同步的数据量,见下面代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
|
//1,对数据进行分片
@Override
public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job) throws IOException {
...
statement = connection.createStatement();
//获取nums
results = statement.executeQuery(getCountQuery());
long count = results.getLong(1);
int chunks = ConfigurationHelper.getJobNumMaps(job);
long chunkSize = (count / chunks);
...
for (int i = 0; i < chunks; i++) {
DBInputSplit split;
if ((i + 1) == chunks) {
split = new DBInputSplit(i * chunkSize, count);
} else {
split = new DBInputSplit(i * chunkSize, (i * chunkSize)
+ chunkSize);
}
splits.add(split);
}
...
}
}
protected String getCountQuery() {
if (dbConf.getInputCountQuery() != null) {
return dbConf.getInputCountQuery();
}
StringBuilder query = new StringBuilder();
query.append("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM " + tableName);
if (conditions != null && conditions.length() > 0) {
query.append(" WHERE " + conditions);
}
return query.toString();
}
//2,读取数据库中的数据
// 根据构造函数创建select 语句,sqoop中分为三种oracle,db2,通用
protected String getSelectQuery() {
StringBuilder query = new StringBuilder();
// Default codepath for MySQL, HSQLDB, etc.
// Relies on LIMIT/OFFSET for splits.
if (dbConf.getInputQuery() == null) {
query.append("SELECT ");
for (int i = 0; i < fieldNames.length; i++) {
query.append(fieldNames[i]);
if (i != fieldNames.length -1) {
query.append(", ");
}
}
query.append(" FROM ").append(tableName);
query.append(" AS ").append(tableName); //in hsqldb this is necessary
if (conditions != null && conditions.length() > 0) {
query.append(" WHERE (").append(conditions).append(")");
}
String orderBy = dbConf.getInputOrderBy();
if (orderBy != null && orderBy.length() > 0) {
query.append(" ORDER BY ").append(orderBy);
}
} else {
//PREBUILT QUERY
query.append(dbConf.getInputQuery());
}
try {
query.append(" LIMIT ").append(split.getLength());
query.append(" OFFSET ").append(split.getStart());
} catch (IOException ex) {
// Ignore, will not throw.
}
return query.toString();
}
// 3,写入hdfs,采用一般的context.write
|
从读取数据库中够着的语句看得出作者是有一番琢磨的,但是个人对构造的数据库语句的执行性能表示不大满意,也可能是出于通用写法,也可能是作者对数据不太了解,eg: 在 oracle 中可以加入 hint 采用直接路径读方式,效率可以提升一个量级。
数据库客户端工具
采用 mysql 提供的客户端工具 sqldump,要使用的前提是集群的机子有安装 mysql 客户端。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
|
// 分片获取的上下限的方式,如下:
protected String getBoundingValsQuery() {
// If the user has provided a query, use that instead.
String userQuery = getDBConf().getInputBoundingQuery();
if (null != userQuery) {
return userQuery;
}
// Auto-generate one based on the table name we've been provided with.
StringBuilder query = new StringBuilder();
String splitCol = getDBConf().getInputOrderBy();
query.append("SELECT MIN(").append(splitCol).append("), ");
query.append("MAX(").append(splitCol).append(") FROM ");
query.append(getDBConf().getInputTableName());
String conditions = getDBConf().getInputConditions();
if (null != conditions) {
query.append(" WHERE ( " + conditions + " )");
}
return query.toString();
}
//2,读取数据,这是最特别的实现,通过构造mysqldump语句导出数据
public void map(String splitConditions, NullWritable val, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
LOG.info("Beginning mysqldump fast path import");
ArrayList<String> args = new ArrayList<String>();
String tableName = conf.get(MySQLUtils.TABLE_NAME_KEY);
// We need to parse the connect string URI to determine the database name.
// Using java.net.URL directly on the connect string will fail because
// Java doesn't respect arbitrary JDBC-based schemes. So we chop off the
// scheme (everything before '://') and replace it with 'http', which we
// know will work.
String connectString = conf.get(MySQLUtils.CONNECT_STRING_KEY);
String databaseName = JdbcUrl.getDatabaseName(connectString);
String hostname = JdbcUrl.getHostName(connectString);
int port = JdbcUrl.getPort(connectString);
if (null == databaseName) {
throw new IOException("Could not determine database name");
}
LOG.info("Performing import of table " + tableName + " from database "
+ databaseName);
args.add(MySQLUtils.MYSQL_DUMP_CMD); // requires that this is on the path.
String password = DBConfiguration.getPassword((JobConf) conf);
String passwordFile = null;
Process p = null;
AsyncSink sink = null;
AsyncSink errSink = null;
PerfCounters counters = new PerfCounters();
try {
// --defaults-file must be the first argument.
if (null != password && password.length() > 0) {
passwordFile = MySQLUtils.writePasswordFile(conf);
args.add("--defaults-file=" + passwordFile);
}
// Don't use the --where="<whereClause>" version because spaces in it can
// confuse Java, and adding in surrounding quotes confuses Java as well.
String whereClause = conf.get(MySQLUtils.WHERE_CLAUSE_KEY, "(1=1)")
+ " AND (" + splitConditions + ")";
args.add("-w");
args.add(whereClause);
args.add("--host=" + hostname);
if (-1 != port) {
args.add("--port=" + Integer.toString(port));
}
args.add("--skip-opt");
args.add("--compact");
args.add("--no-create-db");
args.add("--no-create-info");
args.add("--quick"); // no buffering
args.add("--single-transaction");
String username = conf.get(MySQLUtils.USERNAME_KEY);
if (null != username) {
args.add("--user=" + username);
}
// If the user supplied extra args, add them here.
String [] extra = conf.getStrings(MySQLUtils.EXTRA_ARGS_KEY);
if (null != extra) {
for (String arg : extra) {
args.add(arg);
}
}
args.add(databaseName);
args.add(tableName);
...
// Actually start the mysqldump.
p = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(args.toArray(new String[0]));
...
}
// 3,写入hdfs,这个也是值得说一说地方,作者将导出后的数据,切分成 A,B,C 这种格式(分隔符,可依据传入的参数指定)然后在统一推到hdfs。
private static class CopyingStreamThread extends ErrorableThread {
public static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(
CopyingStreamThread.class.getName());
...
public void run() {
BufferedReader r = null;
...
r = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(this.stream));
// Actually do the read/write transfer loop here.
int preambleLen = -1; // set to this for "undefined"
while (true) {
String inLine = r.readLine();
if (null == inLine) {
break; // EOF.
}
if (inLine.trim().length() == 0 || inLine.startsWith("--")) {
continue; // comments and empty lines are ignored
}
// this line is of the form "INSERT .. VALUES ( actual value text
// );" strip the leading preamble up to the '(' and the trailing
// ');'.
if (preambleLen == -1) {
// we haven't determined how long the preamble is. It's constant
// across all lines, so just figure this out once.
String recordStartMark = "VALUES (";
preambleLen = inLine.indexOf(recordStartMark)
+ recordStartMark.length();
}
// chop off the leading and trailing text as we write the
// output to HDFS.
int len = inLine.length() - 2 - preambleLen;
context.write(inLine.substring(preambleLen, inLine.length() - 2)
+ "\n", null);
counters.addBytes(1 + len);
}
...
}
}
}
|
导出
sqoop 还是提供俩种方式 1,jdbc;2,客户端导出
JDBC
使用 jdbc 导出,使用客户端的 insert 语句,批量插入。比较一般,具体可见 jdbc 批量插入相关章节
使用客户端工具
mapreduce 先将 hdfs 数据写入到本地文件路径,按表名命名的文件,mysqlimport 读取本地文件将输入导出到 mysql
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
|
private void initMySQLImportProcess() throws IOException {
File taskAttemptDir = TaskId.getLocalWorkPath(conf);
this.fifoFile = new File(taskAttemptDir,
conf.get(MySQLUtils.TABLE_NAME_KEY, "UNKNOWN_TABLE") + ".txt");
String filename = fifoFile.toString();
// Create the FIFO itself.
try {
new NamedFifo(this.fifoFile).create();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// Command failed.
LOG.error("Could not mknod " + filename);
this.fifoFile = null;
throw new IOException(
"Could not create FIFO to interface with mysqlimport", ioe);
}
// Now open the connection to mysqlimport.
ArrayList<String> args = new ArrayList<String>();
String connectString = conf.get(MySQLUtils.CONNECT_STRING_KEY);
String databaseName = JdbcUrl.getDatabaseName(connectString);
String hostname = JdbcUrl.getHostName(connectString);
int port = JdbcUrl.getPort(connectString);
if (null == databaseName) {
throw new IOException("Could not determine database name");
}
args.add(MySQLUtils.MYSQL_IMPORT_CMD); // needs to be on the path.
String password = DBConfiguration.getPassword((JobConf) conf);
if (null != password && password.length() > 0) {
passwordFile = new File(MySQLUtils.writePasswordFile(conf));
args.add("--defaults-file=" + passwordFile);
}
String username = conf.get(MySQLUtils.USERNAME_KEY);
if (null != username) {
args.add("--user=" + username);
}
args.add("--host=" + hostname);
if (-1 != port) {
args.add("--port=" + Integer.toString(port));
}
args.add("--compress");
args.add("--local");
args.add("--silent");
// Specify the subset of columns we're importing.
DBConfiguration dbConf = new DBConfiguration(conf);
String [] cols = dbConf.getInputFieldNames();
if (null != cols) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
boolean first = true;
for (String col : cols) {
if (!first) {
sb.append(",");
}
sb.append(col);
first = false;
}
args.add("--columns=" + sb.toString());
}
// Specify the delimiters to use.
int outputFieldDelim = conf.getInt(MySQLUtils.OUTPUT_FIELD_DELIM_KEY,
(int) ',');
int outputRecordDelim = conf.getInt(MySQLUtils.OUTPUT_RECORD_DELIM_KEY,
(int) '\n');
int enclosedBy = conf.getInt(MySQLUtils.OUTPUT_ENCLOSED_BY_KEY, 0);
int escapedBy = conf.getInt(MySQLUtils.OUTPUT_ESCAPED_BY_KEY, 0);
boolean encloseRequired = conf.getBoolean(
MySQLUtils.OUTPUT_ENCLOSE_REQUIRED_KEY, false);
args.add("--fields-terminated-by=0x"
+ Integer.toString(outputFieldDelim, 16));
args.add("--lines-terminated-by=0x"
+ Integer.toString(outputRecordDelim, 16));
if (0 != enclosedBy) {
if (encloseRequired) {
args.add("--fields-enclosed-by=0x" + Integer.toString(enclosedBy, 16));
} else {
args.add("--fields-optionally-enclosed-by=0x"
+ Integer.toString(enclosedBy, 16));
}
}
if (0 != escapedBy) {
args.add("--escaped-by=0x" + Integer.toString(escapedBy, 16));
}
// These two arguments are positional and must be last.
args.add(databaseName);
args.add(filename);
...
// Actually start mysqlimport.
mysqlImportProcess = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(args.toArray(new String[0]));
...
}
|
datax
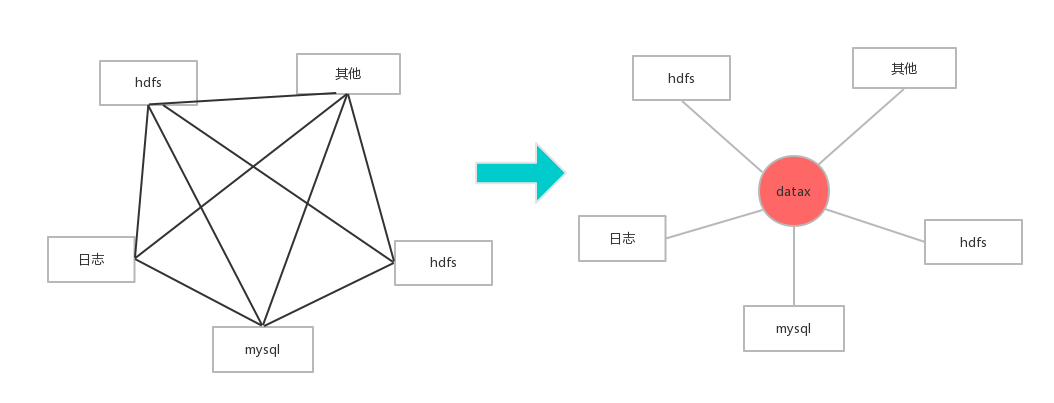
这是阿里开源了一个单机版本的源码,想要达成的一个目标,所有数据的交换都只要 datax 提供一种通用的接口就可以,用起来简单,不需要开发人员在学习 mysql,oracle,mapreduce 等的代码编写,想法很棒。结构如下:  数据的传输全部依赖内存,实现基本原理类似 flume,memorychanne。俩者都有数据丢失可能,在异常情况下。有兴趣的同学可以去看看 flume 的源码。回到导入导出的话题。 在导入和导出,datax 提供了一个统一的模型采用 jdbc 方式去链接。
数据的传输全部依赖内存,实现基本原理类似 flume,memorychanne。俩者都有数据丢失可能,在异常情况下。有兴趣的同学可以去看看 flume 的源码。回到导入导出的话题。 在导入和导出,datax 提供了一个统一的模型采用 jdbc 方式去链接。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
public void startRead(Configuration readerSliceConfig,
RecordSender recordSender,
TaskPluginCollector taskPluginCollector, int fetchSize) {
String querySql = readerSliceConfig.getString(Key.QUERY_SQL);
String table = readerSliceConfig.getString(Key.TABLE);
PerfTrace.getInstance().addTaskDetails(taskId, table + "," + basicMsg);
LOG.info("Begin to read record by Sql: [{}\n] {}.",
querySql, basicMsg);
PerfRecord queryPerfRecord = new PerfRecord(taskGroupId,taskId, PerfRecord.PHASE.SQL_QUERY);
queryPerfRecord.start();
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection(this.dataBaseType, jdbcUrl,
username, password);
// session config .etc related
DBUtil.dealWithSessionConfig(conn, readerSliceConfig,
this.dataBaseType, basicMsg);
int columnNumber = 0;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
rs = DBUtil.query(conn, querySql, fetchSize);
queryPerfRecord.end();
ResultSetMetaData metaData = rs.getMetaData();
columnNumber = metaData.getColumnCount();
//这个统计干净的result_Next时间
PerfRecord allResultPerfRecord = new PerfRecord(taskGroupId, taskId, PerfRecord.PHASE.RESULT_NEXT_ALL);
allResultPerfRecord.start();
long rsNextUsedTime = 0;
long lastTime = System.nanoTime();
while (rs.next()) {
rsNextUsedTime += (System.nanoTime() - lastTime);
this.transportOneRecord(recordSender, rs,
metaData, columnNumber, mandatoryEncoding, taskPluginCollector);
lastTime = System.nanoTime();
}
allResultPerfRecord.end(rsNextUsedTime);
//目前大盘是依赖这个打印,而之前这个Finish read record是包含了sql查询和result next的全部时间
LOG.info("Finished read record by Sql: [{}\n] {}.",
querySql, basicMsg);
}catch (Exception e) {
throw RdbmsException.asQueryException(this.dataBaseType, e, querySql, table, username);
} finally {
DBUtil.closeDBResources(null, conn);
}
}
|
总结
sqoop 和 datax 都采用插件的方式方便用户进行开发新的读写插件,但是基于现有的代码来看,sqoop 的 direct 模式的性能会比 datax 更高,而且 sqoop 是站在大象的肩膀上,稳定性会比单机版的 datax 来得高
扩展
- 构建分布式集群的 datax 构思,
 突发奇想, 如果 datax 不是单机版的我会考虑使用她?简单构思了一下,画了一个草图,来和大家进行讨论讨论,基本流程:每个 node 上都部署了 datax 的服务(需要封装一个在线服务用于启动 datax),定时将 node 状态信息(状态是否存活,内存,cpu 负载,等信息)上报到 consul 配置中心。配置中心的配置由资源管理模块统一进行管理,当作业提交一个导出导出的请求, 先计算分片的数量,以及每个分片需要使用的资源,然后向资源管理模块申请资源,作业管理根据申请到的资源,将启动作业发送到服务注册中心,去启动作业,当作业发生异常情况,反馈给作业管理,进入下一个的待调度列表。
突发奇想, 如果 datax 不是单机版的我会考虑使用她?简单构思了一下,画了一个草图,来和大家进行讨论讨论,基本流程:每个 node 上都部署了 datax 的服务(需要封装一个在线服务用于启动 datax),定时将 node 状态信息(状态是否存活,内存,cpu 负载,等信息)上报到 consul 配置中心。配置中心的配置由资源管理模块统一进行管理,当作业提交一个导出导出的请求, 先计算分片的数量,以及每个分片需要使用的资源,然后向资源管理模块申请资源,作业管理根据申请到的资源,将启动作业发送到服务注册中心,去启动作业,当作业发生异常情况,反馈给作业管理,进入下一个的待调度列表。
- java 调用 shell,命令需要考虑到俩个东西,输入流和异常流。后者是最容易忽略的地方,直接关系着程序的健壮性,sqoop 客户端导入导出给我们提供了一个标准的例子。
- 对数据拆分,然后进行并行操作,这在数据处理领域是一个比较常见的事,共享一个比较经典的例子。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class AccumulateNum implements Serializable {
public final static List<Integer> LST_NUM=new ArrayList();
static {
for(int i=1;i<=100000;i++){
LST_NUM.add(i);
}
}
public static class AccumulateTask extends RecursiveTask<Long> {
//fork的粒度
private final static int THRESHOLD=1000;
private int start;
private int end;
public AccumulateTask(int start,int end){
this.start=start;
this.end=end;
}
@Override
public Long compute() {
long sum=0;
if(end<=start)return sum;
if(end-start<THRESHOLD){
//拆分到理想的粒度进行求和
for(int i=start;i<=end;++i){
sum+= LST_NUM.get(i);
}
}else {
//继续拆分所有求和的数组
int mid=(start+end)/2;
AccumulateTask left = new AccumulateTask(start, mid);
left.fork();
AccumulateTask right = new AccumulateTask(mid + 1, end);
right.fork();
sum=left.join();
sum += right.join();
}
return sum;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int cpu_num=Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
Long startTime=System.nanoTime();
Future<Long> future =pool.submit(new AccumulateTask(0,LST_NUM.size()-1));
Long endTime=System.nanoTime();
System.out.println(future.get());
System.out.println(endTime-startTime+"ns");
pool.shutdown();
pool.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
|
 数据的传输全部依赖内存,实现基本原理类似 flume,memorychanne。俩者都有数据丢失可能,在异常情况下。有兴趣的同学可以去看看 flume 的源码。回到导入导出的话题。 在导入和导出,datax 提供了一个统一的模型采用 jdbc 方式去链接。
数据的传输全部依赖内存,实现基本原理类似 flume,memorychanne。俩者都有数据丢失可能,在异常情况下。有兴趣的同学可以去看看 flume 的源码。回到导入导出的话题。 在导入和导出,datax 提供了一个统一的模型采用 jdbc 方式去链接。 突发奇想, 如果 datax 不是单机版的我会考虑使用她?简单构思了一下,画了一个草图,来和大家进行讨论讨论,基本流程:每个 node 上都部署了 datax 的服务(需要封装一个在线服务用于启动 datax),定时将 node 状态信息(状态是否存活,内存,cpu 负载,等信息)上报到 consul 配置中心。配置中心的配置由资源管理模块统一进行管理,当作业提交一个导出导出的请求, 先计算分片的数量,以及每个分片需要使用的资源,然后向资源管理模块申请资源,作业管理根据申请到的资源,将启动作业发送到服务注册中心,去启动作业,当作业发生异常情况,反馈给作业管理,进入下一个的待调度列表。
突发奇想, 如果 datax 不是单机版的我会考虑使用她?简单构思了一下,画了一个草图,来和大家进行讨论讨论,基本流程:每个 node 上都部署了 datax 的服务(需要封装一个在线服务用于启动 datax),定时将 node 状态信息(状态是否存活,内存,cpu 负载,等信息)上报到 consul 配置中心。配置中心的配置由资源管理模块统一进行管理,当作业提交一个导出导出的请求, 先计算分片的数量,以及每个分片需要使用的资源,然后向资源管理模块申请资源,作业管理根据申请到的资源,将启动作业发送到服务注册中心,去启动作业,当作业发生异常情况,反馈给作业管理,进入下一个的待调度列表。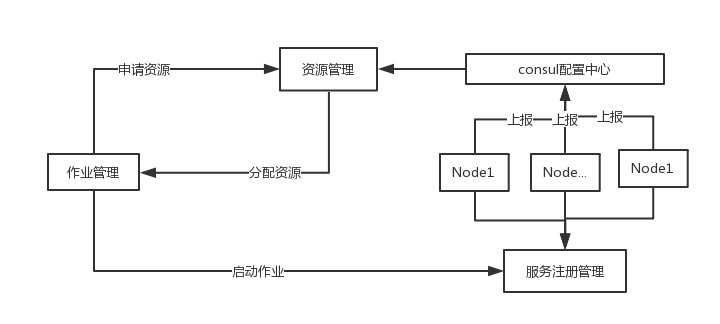 突发奇想, 如果 datax 不是单机版的我会考虑使用她?简单构思了一下,画了一个草图,来和大家进行讨论讨论,基本流程:每个 node 上都部署了 datax 的服务(需要封装一个在线服务用于启动 datax),定时将 node 状态信息(状态是否存活,内存,cpu 负载,等信息)上报到 consul 配置中心。配置中心的配置由资源管理模块统一进行管理,当作业提交一个导出导出的请求, 先计算分片的数量,以及每个分片需要使用的资源,然后向资源管理模块申请资源,作业管理根据申请到的资源,将启动作业发送到服务注册中心,去启动作业,当作业发生异常情况,反馈给作业管理,进入下一个的待调度列表。
突发奇想, 如果 datax 不是单机版的我会考虑使用她?简单构思了一下,画了一个草图,来和大家进行讨论讨论,基本流程:每个 node 上都部署了 datax 的服务(需要封装一个在线服务用于启动 datax),定时将 node 状态信息(状态是否存活,内存,cpu 负载,等信息)上报到 consul 配置中心。配置中心的配置由资源管理模块统一进行管理,当作业提交一个导出导出的请求, 先计算分片的数量,以及每个分片需要使用的资源,然后向资源管理模块申请资源,作业管理根据申请到的资源,将启动作业发送到服务注册中心,去启动作业,当作业发生异常情况,反馈给作业管理,进入下一个的待调度列表。